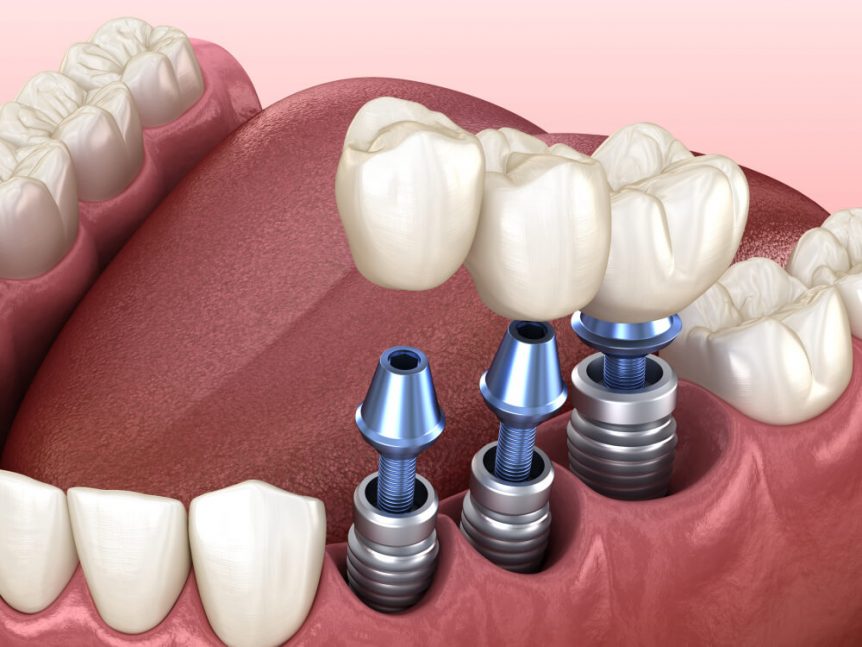
On losing a tooth, bone present in that area undergoes gradual shrinkage. This might be caused by a variety of conditions like injury or trauma, periodontal disease, defective development, and dental caries. Dental implants are prescribed to patients for filling the empty space of a lost tooth.
These cosmetic replacements can prevent further bone loss by preventing natural shrinkage which is synonymous with bone loss and also preserve our jaw bone. Dental implants look and function like real teeth with a titanium root that holds onto the jawbone. These cosmetic replacements can prevent further bone loss by preventing natural shrinkage which is synonymous with bone loss and also preserve our jaw bone. Dental implants look and function like real teeth with a titanium root that holds onto the jawbone.
Patients often struggle to get dental implants as the implants fail to stay in place in the absence of adequate jawbone. However, with the right dentist, implants are possible in most situations. Today we are going to take a look at some of the treatments which are prescribed even when patients don’t have adequate bone for a proper dental implant:
- The bone grafting procedure involves adding bonelike materials to the patient’s jaw. This calls for general anesthesia as the surgeon will have to remove bone from one spot of your body before adding it to your jawbone. If you choose to graft your own bone, then the dentist will procure it from your ramus or chin. In case of any difficulty with procurement from these sources, the dentist will obtain the bone from your shin or hip bone instead.
- A ridge expansion is carried out when the width of the patient’s jaw is not adequate for supporting dental implants. Dentists might allow a few months of healing time or can place implants immediately after the procedure. This procedure can be carried out with local anesthesia.
- The sinus lift process fills a portion of your maxillary sinus for increasing your upper jaw height. Maxillary sinus refers to the area on both the sides of your nose and above your jaw. If your upper jaw’s back part lacks adequate bone for dental implants then dentists will suggest undergoing a sinus lift.
- Distraction osteogenesis refers to a procedure performed for increasing bone size by separating a bone into two pieces. The best thing about this procedure is that it can increase bone size in your preferred direction and this has led to its popularity amongst patients.
A surgeon will insert a titanium connector inside the jawbone and hold the bone in place with pins or screws. Over time the bone will grow taller or broader as the patient unscrews the connector on a daily basis. Ultimately, the connector will be removed by the surgeon and the implant will be inserted by the dentist.
Why there is a need for bone grafting?
The roots of natural teeth are located in the cancellous region of the jawbone called the alveolar bone. This area of the jaw is riddled with blood vessels and nerves. The parameters of the alveolar processes are not constant values and change under the influence of various factors – the intensity of the chewing load, traumatic tooth extraction, endocrine or systemic diseases of the joints and bones. Consider how the absence of chewing pressure affects the jawbone due to tooth extraction.
The roots, due to the constant chewing load, keep the alveolar processes in good shape. With the loss of one or more teeth, the jaw bone in the area of the dentition defect ceases to experience pressure and gradually atrophies. The loss, or resorption, of the bone, begins several months after the extraction of the tooth and can continue until the complete loss of the original volume.
Depending on the localization of the defect, bone resorption occurs in different ways. Due to the fact that the density of the tubular bone in the upper jaw is several times lower than in the lower jaw, atrophy of the upper alveolar process occurs much faster. So, if on the lower jaw the process of bone shrinkage starts after 6-12 months, then on the upper one – already in 2-3 months after tooth extraction.
Dentists distinguish the following types of bone atrophy:
- The alveolar process resolves in width (horizontal atrophy).
- The alveolar process resolves in height (vertical atrophy).
- Resorption occurs in width and height at the same time (combined atrophy).
Depending on the direction, degree, and localization of resorption, various technologies are used to augment bone tissue under a dental implant. The chosen technique of bone grafting, in turn, determines the type of osteoplastic material for bone augmentation.
Final Words
Bone loss can be triggered by a plethora of causes with infection, atrophy, and trauma the most popular ones. It is very normal for bones to progressively deteriorate or shrink when they haven’t been used for long. Old age is synonymous with bone resorption.
Similarly, if your teeth were removed quite some time ago then the bone is most likely to have melted away leaving behind an eggshell of bone. Previously, it was impossible to get dental implants, and patients were advised to go for either extensive bone grafting or had to live with dentures.
However, medical science has advanced substantially and an array of techniques have been added to the arsenal of dentists for curing such problems. Dentists are increasingly relying on various digital marketing techniques for tapping into a greater client base as effective social media management can spread the word in a cost-effective manner.