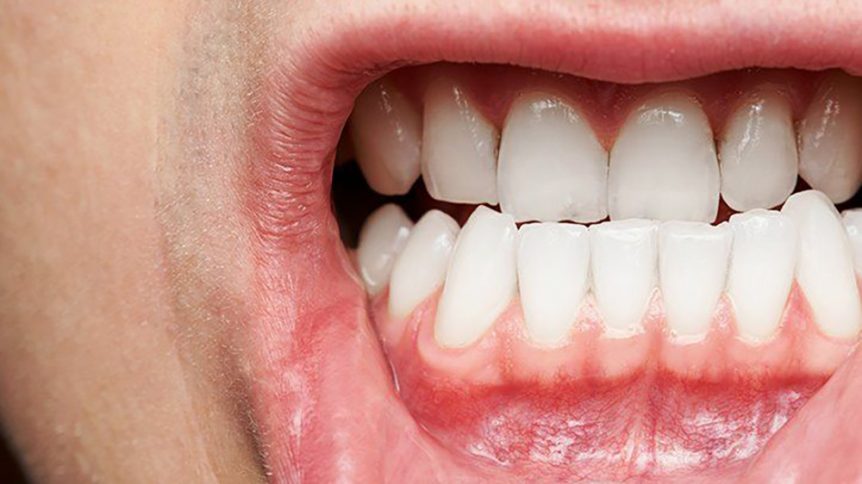
Welcome to our latest blog post, where we’ll be exploring the world of Periodontitis, also known as Gum Disease. If you’ve ever experienced bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, then this is a topic that shouldn’t be ignored. Gum Disease affects millions of people worldwide and if left untreated can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. So whether you’re looking for tips on how to prevent it from happening or seeking treatment options, keep reading! We’ve got all the information you need right here.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums, bones and tissues surrounding the teeth. It’s caused by the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth which can lead to inflammation and irritation of the gums.
The early stages of gum disease are called gingivitis. When left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis. This happens when bacteria invade deeper into the gums causing damage to connective tissues and bone.
Periodontitis can result in tooth loss if not treated promptly. In addition, it has been linked to other health problems such as heart disease, diabetes and respiratory infections. It’s a disturbing fact that gum disease and periodontitis are best friends with other ailments and so it’s important to nip the problem at its bud.
Risk factors for periodontal disease include poor oral hygiene practices such as inadequate brushing or flossing, smoking, genetics and certain medications that reduce saliva flow.
If you suspect you have gum disease or notice any symptoms like bleeding or swollen gums, bad breath or receding gums seek help from your dentist sooner rather than later!
What causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is a serious oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth form plaque on teeth and gums, which can lead to inflammation and eventual damage to the tissues supporting the teeth.
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene is one of the primary causes. When we don’t brush or floss regularly, food particles and bacteria build up in our mouths, leading to plaque formation.
Smoking or using tobacco products increases your risk for gum disease by damaging your gums’ ability to heal from infection. Additionally, certain medications can cause dry mouth, reducing saliva flow that would normally help wash away harmful bacteria.
Genetics may also play a role in developing gum disease. Some individuals are more susceptible than others due to variations in their immune systems’ response to bacterial infections.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can increase inflammation and make it easier for bacteria to develop into gum disease.
In summary, various factors such as poor oral hygiene practices like not brushing properly or frequently enough; smoking/tobacco use; certain medications that reduce salivary flow; genetics; hormonal changes during pregnancy/menopause all contribute towards developing Gum Disease/Periodontitis.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease is an oral health condition that affects the gum tissue and bone structure that supports your teeth. It is a common dental ailment, but many people are unaware of its early symptoms. Here are some warning signs to watch out for:
Bleeding gums: One of the most common symptoms of gum disease is bleeding gums while brushing or flossing. If you notice blood in the sink after brushing, it’s a sign that something isn’t right.
Swollen or red gums: Healthy gums should be pink and firm to touch. If your gums appear swollen or red, it could indicate inflammation caused by bacteria buildup.
Tooth sensitivity: Gum recession exposed tooth roots which can lead to increased tooth sensitivity when consuming hot/cold food and beverages.
Bad breath: Chronic bad breath even after regular brushing indicates bacteria buildup within your mouth affecting your oral hygiene
Loose teeth: As periodontitis progresses into more severe stages, patients may experience loose teeth indicating significant damage to the supporting bone structure surrounding their teeth.
It’s essential to visit a dentist regularly if you’re experiencing any of these symptoms as treating gum disease promptly reduces serious complications in later stages!
Treatment for Gum Disease
Periodontal treatment on gum disease is crucial to prevent further damage and tooth loss. The type of treatment required depends on the severity of your case. If you have a mild form of gum disease, your dentist may recommend non-surgical procedures such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) or local antibiotics.
For moderate to severe cases, surgical treatments may be necessary. These include flap surgery, bone grafts, tissue regeneration, and guided tissue regeneration. In some cases, lasers can also be used for more precise treatment.
After the initial treatment is completed, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly. Your dentist will likely recommend follow-up appointments every three to six months depending on the severity of your condition.
Ignoring gum disease can lead to serious health complications like heart disease and stroke in addition to tooth loss. Seeking professional help at the first sign of symptoms is key to effective treatment and prevention of further damage.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure, and this holds true for gum disease as well. Taking proper care of your oral health can help prevent gum disease from developing in the first place.
To start with, maintaining a good oral hygiene routine is key. This includes brushing twice daily for at least two minutes each time and flossing once a day to remove any food particles or plaque that may have accumulated between teeth.
In addition to regular dental cleaning appointments, it’s important to also watch what you eat. A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates can increase the risk of gum disease by promoting bacterial growth in the mouth. Instead, opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of periodontal disease as well as other health issues such as cancer and heart disease. Avoiding smoking or quitting altogether is one way to reduce your chances of developing gum disease.
Stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation or yoga can help promote overall health including oral health by reducing inflammation throughout the body which could lead to fewer complications related to periodontitis later on down the line.
Conclusion
Maintaining good oral health is crucial for overall well-being, and gum disease or periodontitis can significantly compromise it. It’s essential to understand the causes of gum disease and its symptoms to stay ahead of the problem.
Poor dental hygiene habits, smoking, genetics, diabetes, hormonal changes in women, and certain medications are some common culprits behind this condition.
If left untreated, periodontitis can cause severe damage to teeth and gums leading to tooth loss. However, with proper treatment like scaling and root planing or surgery in severe cases along with good oral care practices at home such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help you prevent further progression of the disease.
Lastly, always remember that prevention is always better than cure so make sure you schedule regular dental check-ups every six months. By following these simple measures regularly you will not only keep your mouth healthy but also improve your overall health. So be mindful about your oral health because a healthy smile reflects a happy soul!